总结数组与链表的区别[转载]
总结
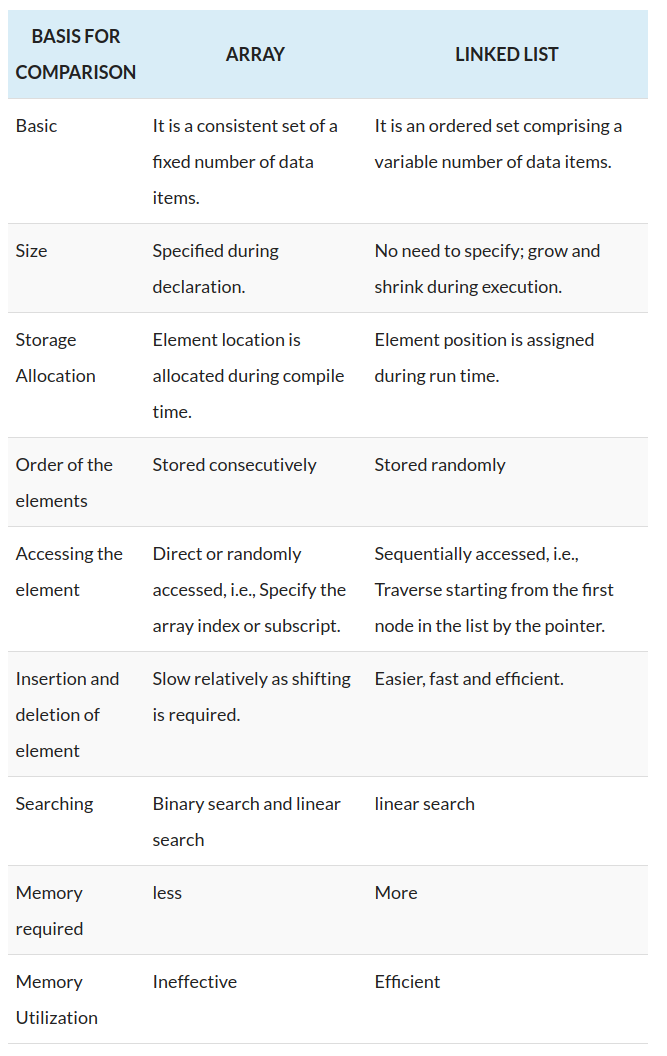
| 比较项目 | 数组 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 大小定义 | 声明时给定好,增删会重新定义数组大小 | 无需指定,在执行过程中自行增长和收缩 |
| 元素位置 | 编译时分配 | 运行时分配 |
| 元素顺序 | 连续空间 | 随机空间 |
| 增 | 时间复杂度O(n), 空间复杂度O(n) | 时间复杂度O(1), 空间复杂度O(1) |
| 删 | 时间复杂度O(n), 空间复杂度O(n) | 时间复杂度O(1), 空间复杂度O(1) |
| 查 | 时间复杂度O(1), 空间复杂度O(1) | 时间复杂度O(n), 空间复杂度O(1) |
注:
-
数组的增删操作,平均时间复杂度最好情况是在最后一个元素,最坏情况是在第一个元素,平均为O(n/2),所以等同于O(n),空间复杂度类似
-
链表的增删操作,不考虑遍历到需要更改的元素位置所需要的时间复杂度的,所以时间复杂度可以认为是O(1)
-
因为数组在内存空间是连续的,所以内存利用率,数组要低于链表
-
注重数据的随机访问效率的话,不考虑数据的增删操作,选择数组
-
经常增加删除数据,又不是太在意数据访问时间,选择链表
下面内容转自Difference Between Array and Linked List (with Comparison Chart) - Tech Differences 侵删
The major difference between Array and Linked list regards to their structure. Arrays are index based data structure where each element associated with an index. On the other hand, Linked list relies on references where each node consists of the data and the references to the previous and next element.
Basically, an array is a set of similar data objects stored in sequential memory locations under a common heading or a variable name.
While a linked list is a data structure which contains a sequence of the elements where each element is linked to its next element. There are two fields in an element of linked list. One is Data field, and other is link field, Data field contains the actual value to be stored and processed. Furthermore, the link field holds the address of the next data item in the linked list. The address used to access a particular node is known as a pointer.
Another significant difference between an array and linked list is that Array has a fixed size and required to be declared prior, but Linked List is not restricted to size and expand and contract during execution.
Comparison Chart
Definition of Array
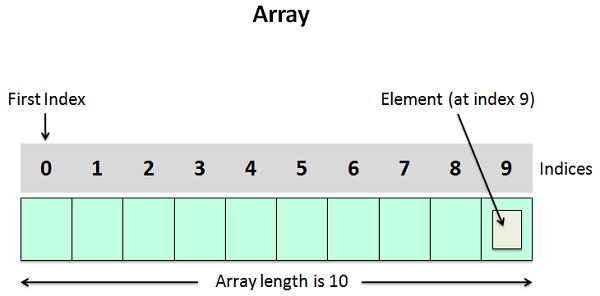
An array is defined as a set of a definite number of homogeneous elements or data items. It means an array can contain one type of data only, either all integers, all floating-point numbers, or all characters. Declaration of an array is as follows:
int a [10];
Where int specifies the data type or type elements array stores. “a” is the name of an array, and the number specified inside the square brackets is the number of elements an array can store, this is also called size or length of the array.
Points to Ponder
Let us look at some of the concepts to be remembered about arrays:
- The individual elements of an array can be accessed by describing the name of the array, followed by index or subscript (determining the location of the element in the array) inside the square brackets. For example, to retrieve 5th element of the array, we need to write a statement a[4].
- In any case the elements of an array will be stored in a consecutive memory location.
- The very first element of the array has index zero [0]. It means the first and last element will be specified as a[0], and a[9] respectively.
- The number of elements that can be stored in an array, i.e., the size of an array or its length is given by the following equation: (upper bound-lower bound) + 1 For the above array, it would be (9-0) + 1 =10. Where 0 is the lower bound of the array, and 9 is the upper bound of the array.
- Arrays can be read or written through the loop. If we read the one-dimensional array, it requires one loop for reading and other for writing (printing) the array, for example: a. For reading an array for ( i= 0; i <= 9; i++) { scanf ( “%d”, &a[ i ] ) ; } b. For writing an array for (i = 0 ; i <= 9 ; i++) {printf ( “%d”, a[ i ] ) ; }
- In the case of a 2-D array, it would require two loops and similarly n-dimensional array would need n loops.
Operations performed on arrays
- Creation of array
- Traversing an array
- Insertion of new elements
- Deletion of required elements.
- Modification of an element.
- Merging of arrays
Example
The following program illustrates the reading and writing of the array.
|
|
Definition of Linked List
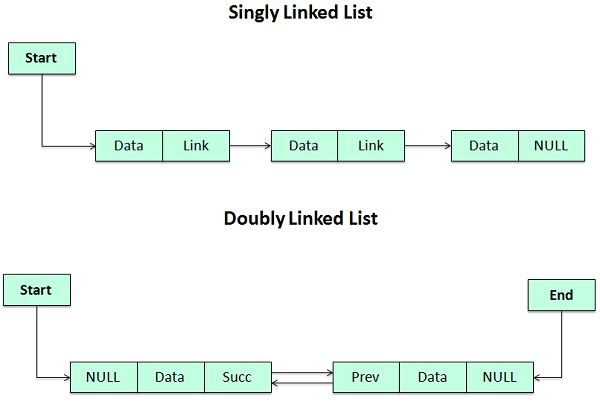
Linked list is a particular list of some data elements linked to one other. In this every element point to the next element which represents the logical ordering. Each element is called a node, which has two parts.
INFO part which stores the information and POINTER which points to the next element. As you know for storing address, we have a unique data structures in C called pointers. Hence the second field of the list must be a pointer type.
Types of linked lists are Singly-linked list, Doubly linked list, Circular linked list, Circular double linked list.
Operations performed on Linked List
- Creation
- Traversing
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Searching
- Concatenation
- Display
Example
The following snippet illustrates the creation of a linked list:
|
|
Key Differences Between Array and Linked List
- An array is the data structure contains a collection of similar type data elements whereas the Linked list is considered as non-primitive data structure contains a collection of unordered linked elements known as nodes.
- In the array the elements belong to indexes, i.e., if you want to get into the fourth element you have to write the variable name with its index or location within the square bracket. In a linked list though, you have to start from the head and work your way through until you get to the fourth element.
- While accessing an element array is fast while Linked list takes linear time so, it is quite bit slower.
- Operations like insertion and deletion in arrays consume a lot of time. On the other hand, the performance of these operations in Linked lists is fast.
- Arrays are of fixed size. In contrast, Linked lists are dynamic and flexible and can expand and contract its size.
- In an array, memory is assigned during compile time while in a Linked list it is allocated during execution or runtime.
- Elements are stored consecutively in arrays whereas it is stored randomly in Linked lists.
- The requirement of memory is less due to actual data being stored within the index in the array. As against, there is a need for more memory in Linked Lists due to storage of additional next and previous referencing elements.
- In addition memory utilization is inefficient in the array. Conversely, memory utilization is efficient in the array.
Conclusion
Array and Linked lists are the types of data structures differ in their structure, accessing and manipulation methods, memory requirement and utilization. And have particular advantage and disadvantage over its implementation. Consequently, either one can be used as per need.