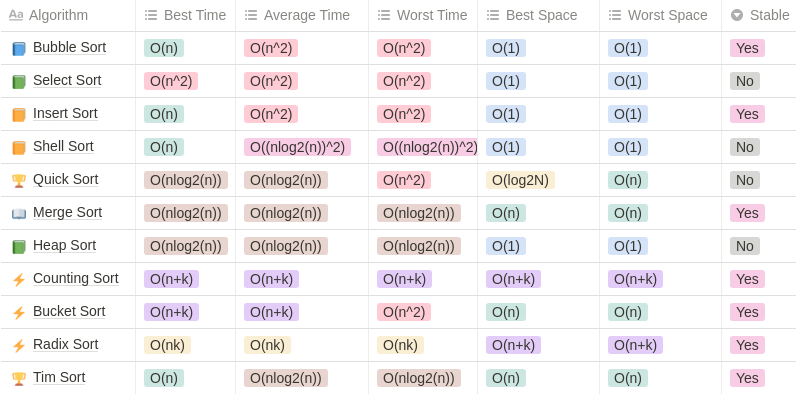
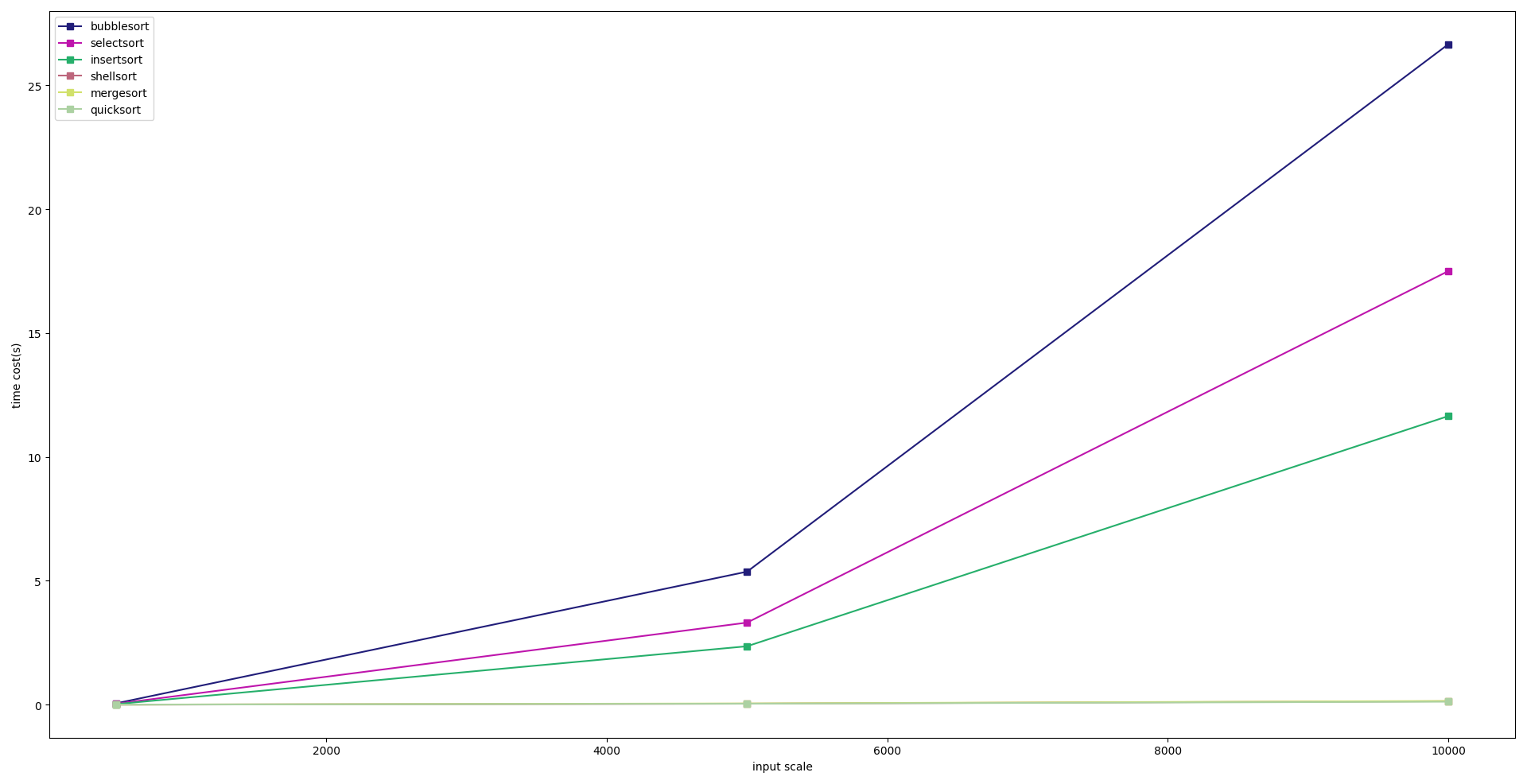
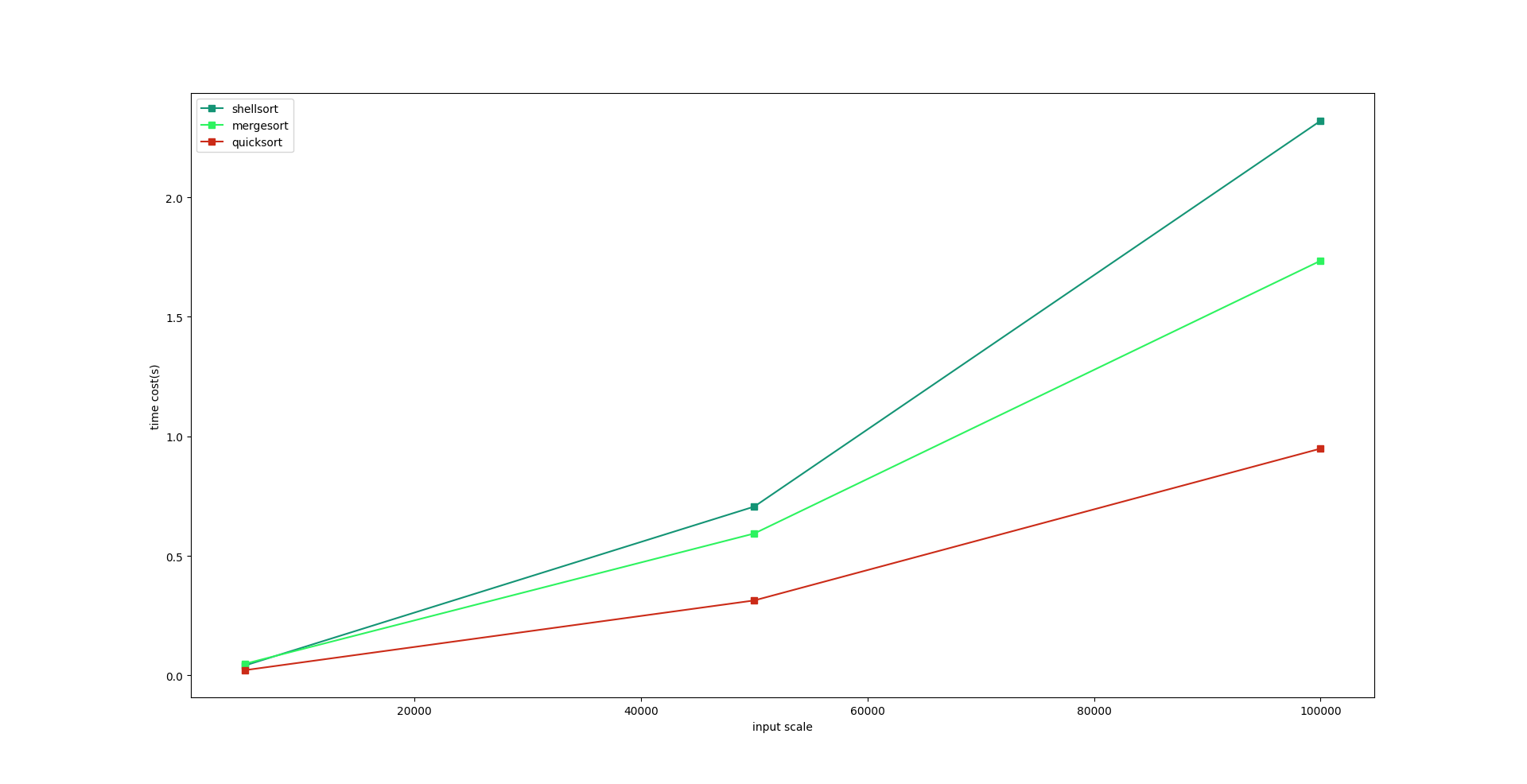
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
|
import numpy as np
from time import process_time
from typing import List
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
class Sorting:
def __init__(self, method: str):
self.easy_samples = np.random.randint(0, 100000, 5000)
self.medium_samples = np.random.randint(0, 100000, 50000)
self.hard_samples = np.random.randint(0, 100000, 100000)
self.start_time = process_time()
self.method = getattr(self, method)
def timeit(self):
return float('%.4f' % (process_time() - self.start_time))
def sort(self):
# print('---------------- Easy Test -------------------')
easy_nums = self.method(self.easy_samples)
t1 = self.timeit()
# print('---------------- Medium Test -------------------')
medium_nums = self.method(self.medium_samples)
t2 = self.timeit()
# print('---------------- Hard Test -------------------')
hard_nums = self.method(self.hard_samples)
t3 = self.timeit()
assert self.checksort(easy_nums)
assert self.checksort(medium_nums)
assert self.checksort(hard_nums)
return [t1, t2, t3], [self.easy_samples.shape, self.medium_samples.shape, self.hard_samples.shape]
@staticmethod
def checksort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
if nums[i] > nums[i + 1]:
return False
return True
@staticmethod
def bubblesort(nums: List) -> List:
length = len(nums)
for i in range(1, length):
sort_over = True
for j in range(length - i):
if nums[j] > nums[j + 1]:
nums[j], nums[j + 1] = nums[j + 1], nums[j]
sort_over = False
if sort_over:
return nums
return nums
@staticmethod
def selectsort(nums: List) -> List:
length = len(nums)
for i in range(length):
min_id = i
for j in range(i, length):
min_id = j if nums[j] < nums[min_id] else min_id
if min_id != i: # 判断是否是当前元素最小,是的话就不用交换
nums[min_id], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[min_id]
return nums
@staticmethod
def insertsort(nums: List) -> List:
length = len(nums)
for i in range(length):
cur_val = nums[i]
last_id = i - 1
while last_id >= 0 and nums[last_id] > cur_val:
nums[last_id + 1] = nums[last_id]
last_id -= 1
nums[last_id + 1] = cur_val
return nums
@staticmethod
def shellsort(nums: List) -> List:
length = len(nums)
gap = length
while gap > 0:
for i in range(gap, length):
cur_val = nums[i]
last_id = i - gap
while last_id >= 0 and nums[last_id] > cur_val:
nums[last_id + gap] = nums[last_id]
last_id -= gap
nums[last_id + gap] = cur_val
gap //= 2
return nums
@staticmethod
def mergesort(nums: List) -> List:
def merge(arr_, left_, mid_, right_, tmp_):
ptr1, ptr2, index = left_, mid_+1, 0
# 遍历ptr1和ptr2,装填res_数组,直到ptr1或ptr2到头
for i in range(right_-left_+1):
if ptr1 > mid_ or ptr2 > right_:
break
if arr_[ptr1] <= arr_[ptr2]: # 注意 '=' 才能让排序稳定
tmp_[index] = arr_[ptr1]
ptr1, index = ptr1+1, index+1
else:
tmp_[index] = arr_[ptr2]
ptr2, index = ptr2+1, index+1
# 调用extend将剩余元素都装入数组res中
if ptr1 > mid_:
tmp_[index:right_-left_+1] = arr_[ptr2:right_+1]
if ptr2 > right_:
tmp_[index:right_-left_+1] = arr_[ptr1:mid_+1]
# 改变arr_区间中的元素顺序
arr_[left_:right_+1] = tmp_[:right_-left_+1]
def mergesort_rec(arr, left, right, tmp):
if left >= right:
return
mid = (right + left) // 2
mergesort_rec(arr, left, mid, tmp)
mergesort_rec(arr, mid+1, right, tmp)
merge(arr, left, mid, right, tmp)
length = len(nums)
mergesort_rec(nums, 0, length-1, [0]*length)
return nums
@staticmethod
def quicksort(nums: List) -> List:
def partition(left, right):
i, pivot = left, nums[left] # 这里记录下左指针指向的值,后面比较时不需要重复索引,可以有效节省时间
while left < right:
while left < right and nums[right] >= pivot:
right -= 1
while left < right and nums[left] <= pivot:
left += 1
nums[left], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[left]
nums[i], nums[left] = nums[left], pivot
return left
def sort(start, end):
if start >= end:
return []
pivot = partition(start, end)
sort(start, pivot-1)
sort(pivot+1, end)
sort(0, len(nums)-1)
return nums
def plot_and_show(sorting_algo, res, size):
x = size # 点的横坐标
def randomcolor():
colorArr = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']
color = ""
for i in range(6):
color += colorArr[random.randint(0, 14)]
return "#" + color
for i, cur in enumerate(res):
print(cur)
plt.plot(x, cur, 's-', color=randomcolor(), label=sorting_algo[i]) # s-:方形
plt.xlabel("input scale") # 横坐标名字
plt.ylabel("time cost(s)") # 纵坐标名字
plt.legend(loc="best") # 图例
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
sorting_algo = [
'bubblesort',
'selectsort',
'insertsort',
'shellsort',
'mergesort',
'quicksort',
]
res = []
size = []
for cur_algo in sorting_algo:
sort_ = Sorting(method=cur_algo)
t, size = sort_.sort()
res.append(t)
plot_and_show(sorting_algo, res, size)
|